www.met.ie display issues - blank map / hourly forecast won't change / clear browser cache
The place name name at the top of our homepage is the location for the hourly forecast under it, and the pointer on the map. Click on it to add a different location. However if the location will not change and/or it shows an incorrect Regional text forecast location, this issue can be reset by clearing the cache/data for www.met.ie only on your web browser.
Clearing the cache/data can also resolve a blank map on your web browser.
The hourly forecasts on the Met Éireann App is not affected by this.
Here are some suggested methods to resolve this for some of the more popular browsers:
Chrome on desktop
Open a new tab on the Chrome browser and copy and paste this line into the address bar at the top:
chrome://settings/content/siteDetails?site=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.met.ie
Click Clear Data and Reset Permissions.
Then open a new tab and go to our website https://www.met.ie/
It should act like it is the first time visiting our website, the cookie acceptance request and optional forecast location request will appear.
Chrome on Android
Open the Google Chrome browser on a smartphone/tablet and type in www.met.ie in the address bar and enter. Check the website is opened in Chrome (tap 3 horizontal dots and select ‘open in browser’).
Tap the 3 vertical dots in the top right. Tap Settings – Site Settings – All sites. Tap the magnifier and write in met.ie. Select www.met.ie and select Clear & Reset. Then open Chrome again and go to www.met.ie. This resets our website’s location access request and cookie acceptance request, it should ask if you want to accept those. This should be sufficient to remove the forecast location issue. These instructions may vary on different device manufacturers.
Microsoft Edge on desktop
Open a tab on Edge and add this line to the address bar and press enter:
edge://settings/content/cookies/siteData?searchSubpage=met.ie
Add click Remove all shown.
Then reset site permissions, copy and past this line to the address bar and enter:
edge://settings/content/all
and add met.ie to the Search bar.
Click the arrow across from met.ie and then click Reset permissions. Then open www.met.ie, the cookie and location popup options will appear, please make your preferred selections.
Safari on desktop
When you are in Safari, in the top left click Safari – Preferences – Privacy – Manage Website Data – search met.ie and delete data. Then open a new tab and go to https://www.met.ie/
Safari on iPhone/iPad
Go to the phone Settings – Safari – Advanced – Website Data – search met.ie and swipe across and Delete. Then go on Safari and open a new tab and enter www.met.ie .
Firefox
To clear the met.ie data on Firefox, open a new tab there and paste this into the address bar:
about:preferences#privacy
Under Cookies and Site Data click Manage Data, add met.ie to the Search web sites line, click on met.ie and click Remove Selected. Click Save Changes and Remove to close that. Then scroll down to Permissions. Click Locations Settings, add met.ie and click Remove Web Site, Save Changes.
Then open a new tab on Firefox and type in www.met.ie to the address bar and enter. This will act like it’s the first time you are visiting our website.
Please Contact us on digital.queries@met.ie if you are experiencing further issues.
Common Rainfall Radar Queries
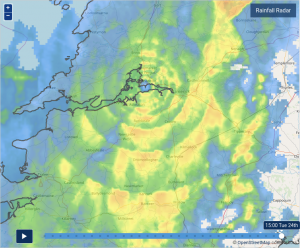
The latest Rainfall Radar showing live precipitation and the last 90 minutes’ precipitation over Ireland, updated every 5 minutes. Precipitation can be rain, hail or snow. Rainfall radar does not detect low lying precipitation, such as drizzle. Images are a combination of Met Éireann and Met Office radar in Dublin, Shannon, Castor Bay in Co. Armagh and in Wales, when available. Lightning strikes, when they occur, are displayed as a cross. Initially they are red but change to orange and then yellow after a period, then disappear.
As mentioned above, the radar does not detect low lying precipitation such as drizzle, this is due to a number of reasons – primarily because radar antenna point upwards and may miss low level precipitation occurring under its detection area; also distance from the radar and topographical features can limit and hinder the precipitation it detects.
Rainfall radar systems are subject to frequent maintenance checks, individual units are powered off during these times, this will affect and reduce the radar images in that surrounding area. Maintenance notices are posted on a banner on www.met.ie, the Met Éireann app and on our Twitter page to inform the public about the outage.
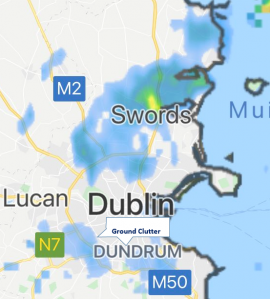
Miscellaneous rainfall images may appear on the radar map from time to time, examples are below:
- ‘ground clutter’ may appear, this is usually apparent in various parts of Co. Dublin. It is a ‘term used for unwanted echoes in electronic systems, particularly in reference to radars. Such echoes are typically returned from ground, sea, rain, animals/insects, chaff and atmospheric turbulences..’ – Wikipedia . It is not real precipitation and should be ignored. We advise to play the last few images of the animation, this will show the movement of any genuine precipitation images that the radar has processed.
- Bright Bands may also occur as circles of precipitation around a radar, often in winter months due to reflectivity of wintry types of precipitation at higher levels in the atmosphere.
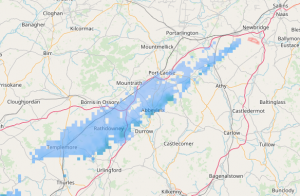
- Spokes can appear as long shadows of ‘rain’, this can happen when there is some interference to the radar signal. It is not real precipitation and should be ignored.
They are common artefacts or false echoes of rainfall radar systems and should be ignored if possible. They are present on our radar map due to our low level filtering which allows finer precipitation to appear on the radar image, which we feel is of utmost benefit to the public, despite the trade off by having the false echoes. There is no need to contact us regarding them.
Weather Warnings for Northern Ireland
Met Éireann do not issue weather warnings for Northern Ireland, but we do display issued Northern Ireland warnings which are issued by the UK Met Office www.metoffice.gov.uk in the United Kingdom. Met Éireann display current weather warnings for Northern Ireland on our weather warnings page and on the Met Éireann app on the map along with the warning details. This is to provide a clear, authoritative one-stop shop for easy and reliable access to the latest weather warnings for the Island of Ireland. In particular, it is hoped that this all-Ireland warnings display will promote citizen and societal safety in border regions.
Official weather warnings for each country are issued by the National Meteorological Service.
Met Éireann issues warnings for Ireland (excluding Northern Ireland) and the Met Office in the UK issues warnings for Northern Ireland, Scotland, Wales and England.
An Orange warning is referred to as Amber for Northern Ireland as this is the colour coding used by the UK Met Office, as in Yellow/Amber/Red, as opposed to the labels Yellow/Orange/Red as used by Met Éireann.
Given our close geographical locations and frequently shared weather systems, Met Éireann and the UK Met Office have ongoing collaboration on the forecasting and naming of storms.
How can I make a Freedom of Information (FOI) request to Met Éireann?
Freedom of Information(FOI) request form is available here
What do all the weather symbols mean?
Here is a list of the weather symbols used by Met Éireann and their description
Day |
Night |
Description |
 |
 |
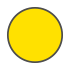
Sun/Clear sky |
 |
 |
Fair |
| Partly Cloudy | ||
 |
 |
Cloudy |
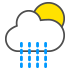 |
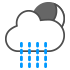 |
Light rain showers |
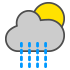 |
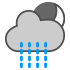 |
Rain showers |
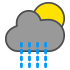 |
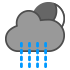 |
Heavy rain showers |
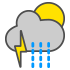 |
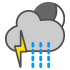 |
Rain showers and thunder |
 |
 |
Sleet showers |
 |
 |
Snow showers |
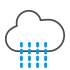 |
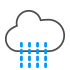 |
Light rain/Drizzle |
 |
 |
Rain |
 |
 |
Heavy rain |
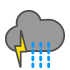 |
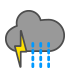 |
Heavy rain and thunder |
 |
 |
Sleet |
 |
 |
Snow |
 |
 |
Snow and thunder |
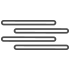 |
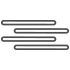 |
Fog/Mist/Haze/Freezing Fog |
 |
 |
Sleet showers and thunder |
 |
 |
Snow showers and thunder |
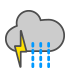 |
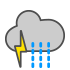 |
Rain and thunder |
 |
 |
Sleet and thunder |
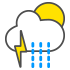 |
 |
Light rain showers and thunder |
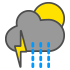 |
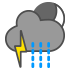 |
Heavy rain showers and thunder |
 |
 |
Light sleet showers and thunder |
 |
 |
Heavy sleet showers and thunder |
 |
 |
Light snow showers and thunder |
 |
 |
Heavy snow showers and thunder |
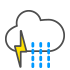 |
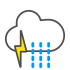 |
Light rain and thunder and/or lightning |
 |
 |
Light sleet and thunder |
 |
 |
Heavy sleet and thunder |
 |
 |
Light snow and thunder |
 |
 |
Heavy snow and thunder |
 |
 |
Light rain showers |
 |
 |
Light sleet showers |
 |
 |
Heavy sleet showers/Freezing rain |
 |
 |
Light snow showers |
 |
 |
Heavy snow showers |
 |
 |
Light sleet |
 |
 |
Heavy sleet |
 |
 |
Light snow |
 |
 |
Heavy snow |
 |
 |
Light Hail Shower |
 |
 |
Heavy Hail Shower |
Note: Some symbols are replicated for similar weather events
Where are the observing stations in Met Éireann?
Met Éireann Headquarters is located at Glasnevin Hill, Dublin 9. Observing stations are in the following places:
Information on the Met Éireann website and app
If you have any queries on using our new website and app please check the guide page first
Wind Barbs
Wind barbs are a convenient way to represent both wind direction and speed. Wind barbs have three parts: a dot, a staff and feathers or flags. The staff part of a wind barb shows wind direction. One long barb is used to indicate each 10 knots with the short barb representing 5 knots. At 50 knots, the barbs changes to a pennant. For wind speeds higher than 50 knots, long and short barbs are used again in combination with the pennant(s).
Wind Barb |
Knot |
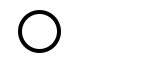 |
Calm |
 |
2 |
 |
5 |
 |
10 |
 |
15 |
 |
20 |
 |
25 |
 |
30 |
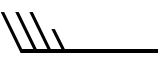 |
35 |
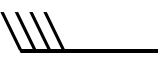 |
40 |
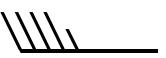 |
45 |
 |
50 |
 |
55 |
 |
60 |
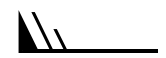 |
65 |
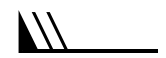 |
70 |
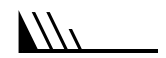 |
75 |
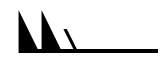 |
105 |
What are the different kinds of meteorological instruments and what do they measure?
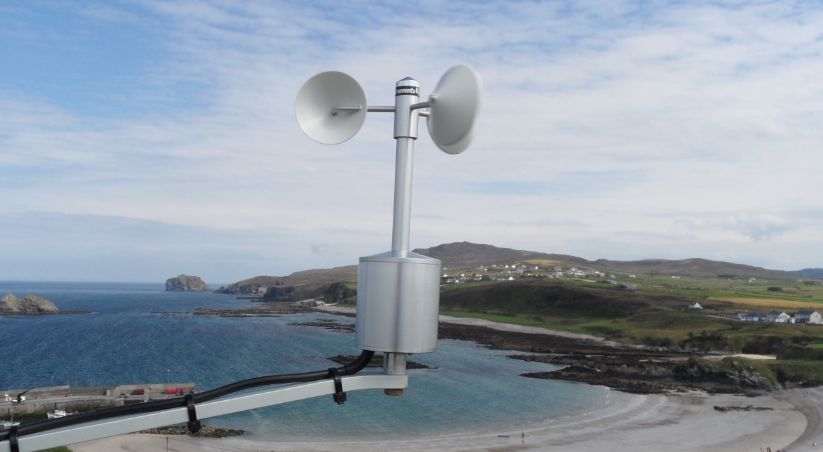
Anemometer: this instrument measures both the wind speed and direction.

Barometer: measures the atmospheric pressure.
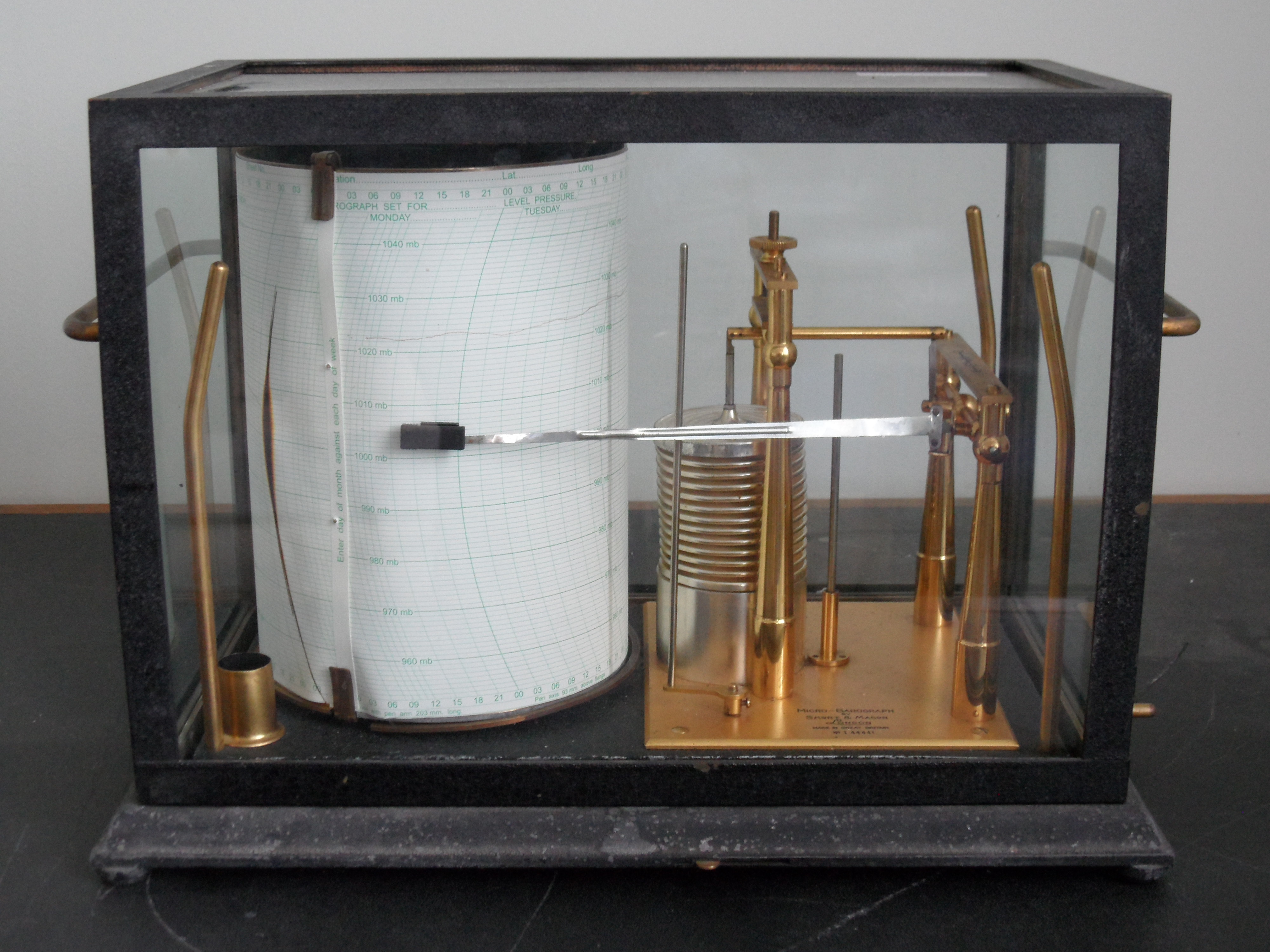
Ceilometer: measures the base of the cloud height.
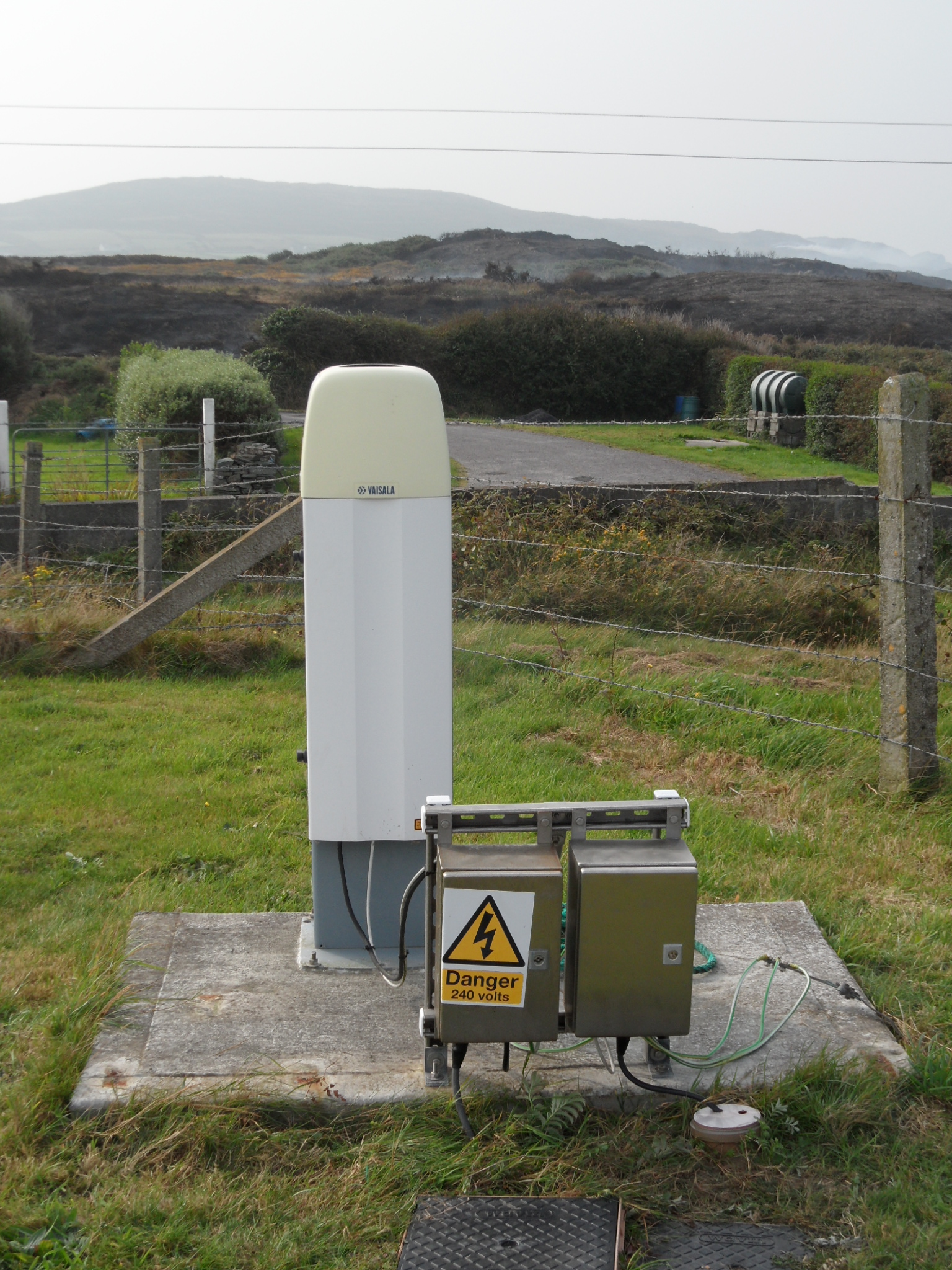

Hygrometer: measures the humidity of the air.
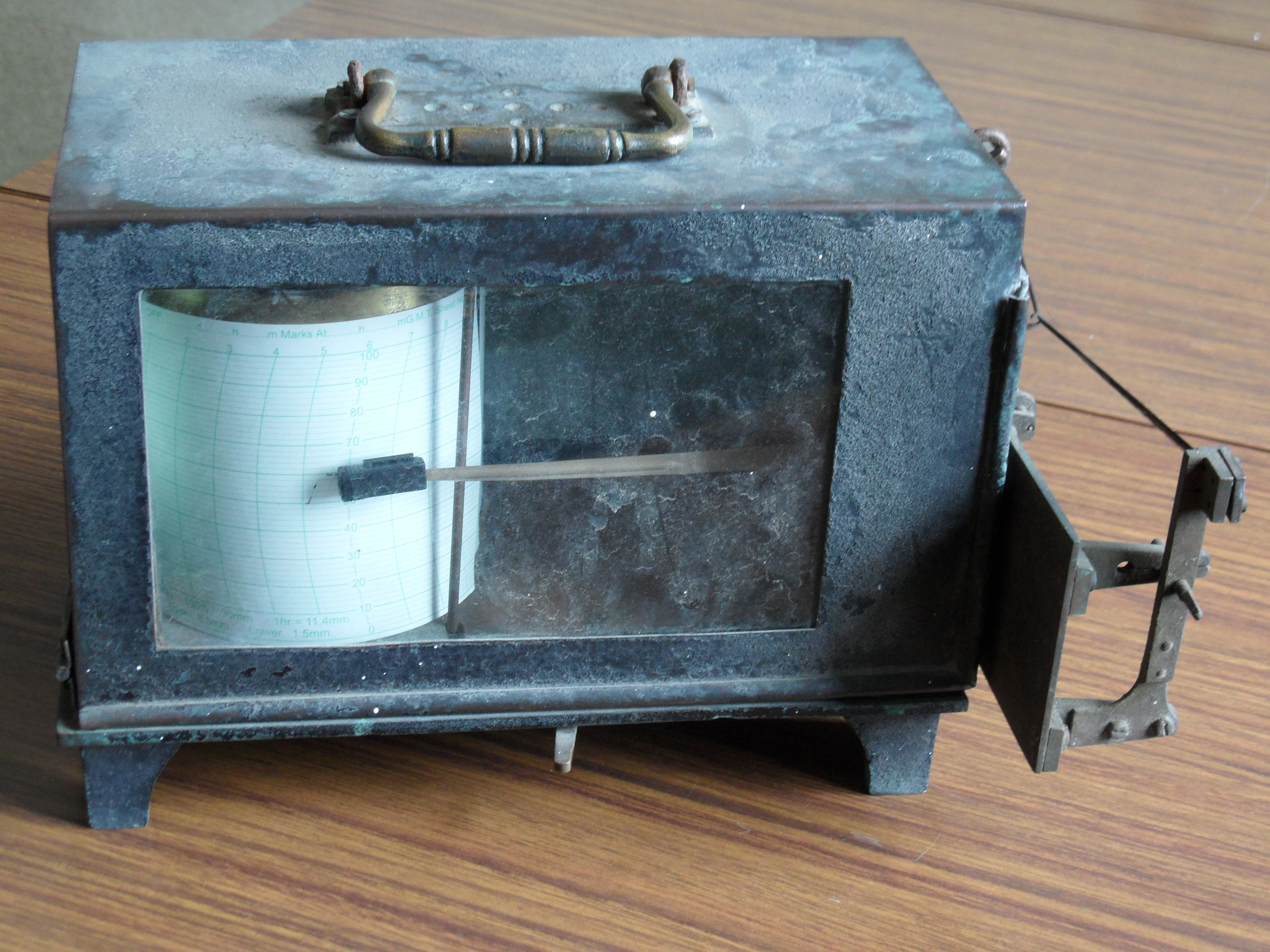

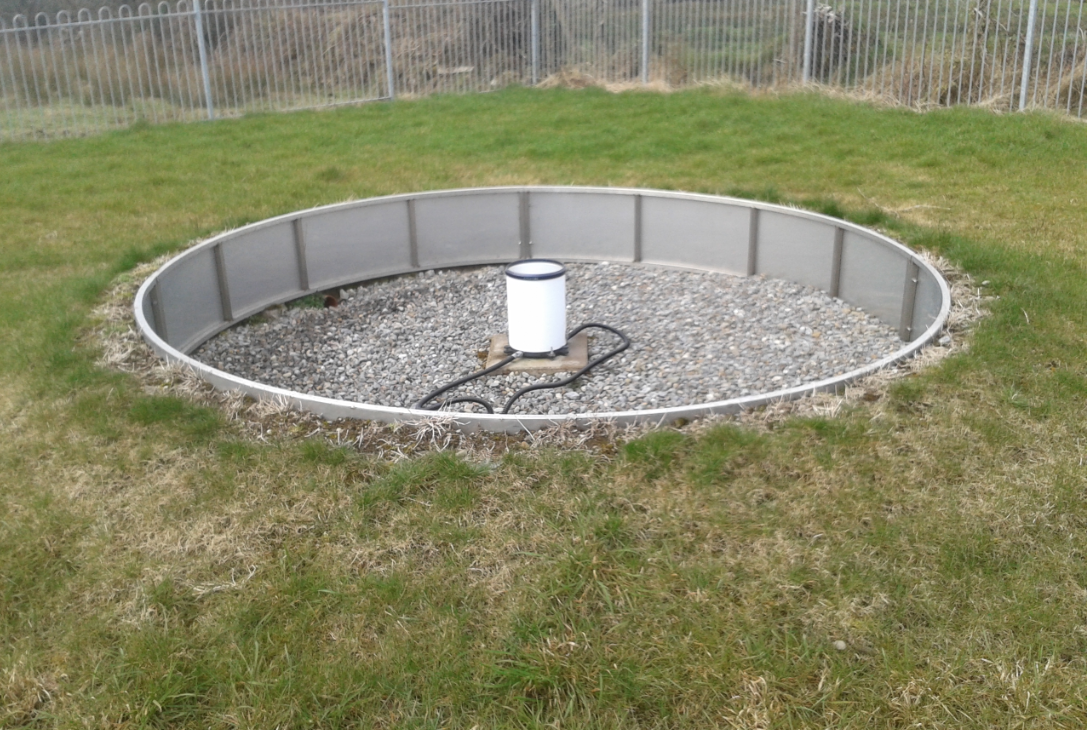
Rain-gauge: measures the amount of precipitation.

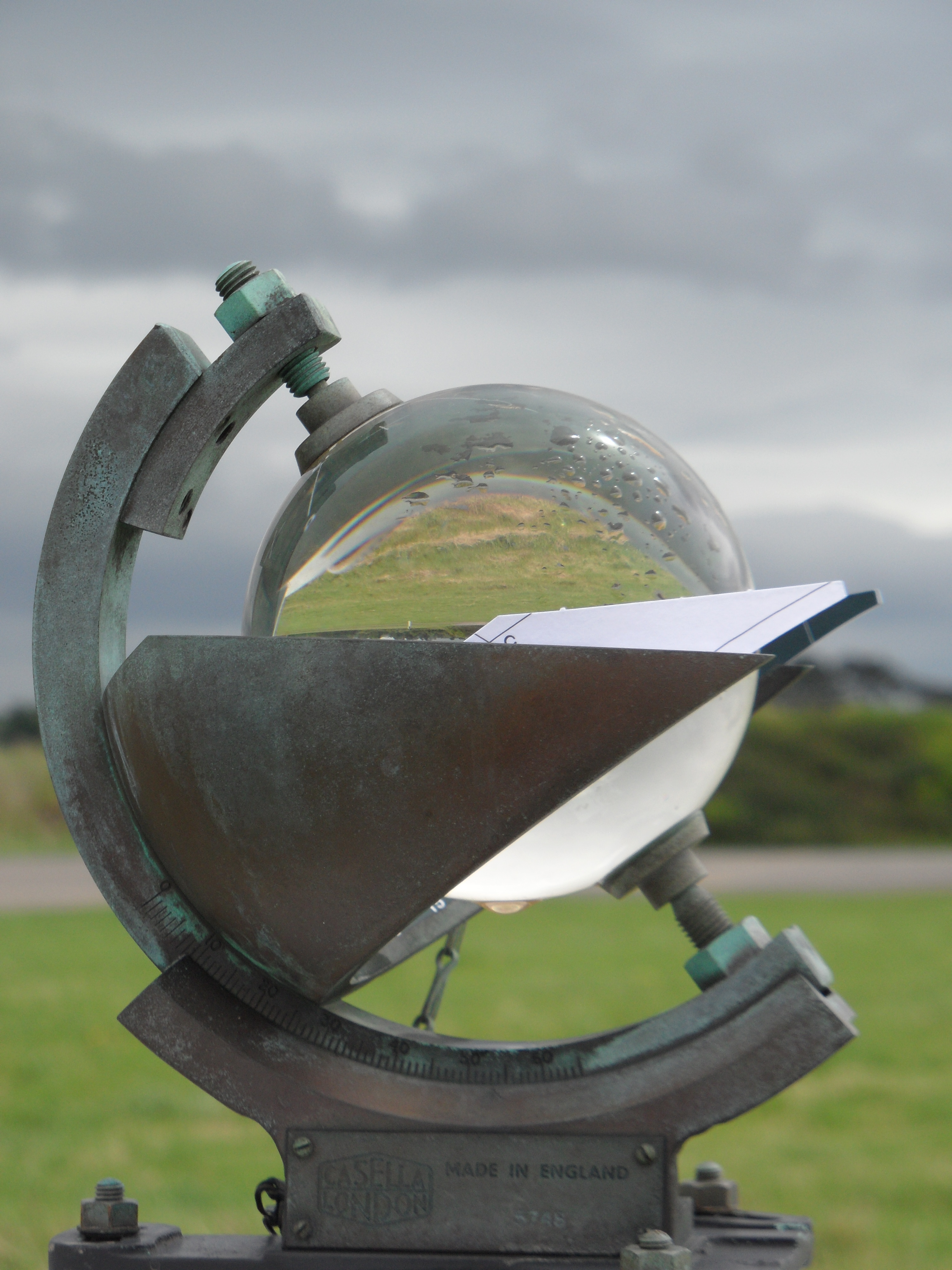
Sunshine recorder: measures the duration of sunshine.

Stevenson-screen: A type of wooden louvered rectangular box which houses maximum and minimum (centre) and wet and dry bulb thermometers.

Figure 3: Stevenson screen. This shields the meteorological instruments inside against precipitation and direct heat radiation.
What do all those weather terms mean?
- Anticyclone: Region of the atmosphere where the pressures are high relative to those in the surrounding region at the same level.
- Depression: Region of the atmosphere in which the pressures are lower than those of the surrounding region at the same level. This is the opposite of an Anticyclone.
- Cyclone:A severe type of tropical storm with very low atmospheric pressure at the centre and strong winds blowing around it.
- Gulf Stream: A current of warm surface ocean water in the North Atlantic flowing from the Gulf of Mexico towards northwest Europe. It has an important influence in maintaining relatively mild winters in Ireland.
- hectoPascal: Unit of pressure, equivalent to a Millibar.
- Isobar: Line joining points of equal pressure
- Isohyet: Line joining points of equal precipitation amount recorded during a specific period.
- Isotach: Line joining points of equal wind speed
- Isotherm: Line joining points of equal air temperature.
How can I find out more about weather statistics?
Check Recent Weather for yesterday’s weather and monthly data for the year so far.
Check the Climate section (30 year averages) for:
- Monthly mean Air Temperatures
- Mean Maximum and Minimum Air Temperatures
- Wind speeds
- Rainfall, Sunshine, Humidity and other climatological means and extremes
If you require more detailed information such as weather reports, expert opinion or detailed analyses, please contact our Climate and Observations Division.
A fee may apply for the provision of the above.
What is the difference between climate and weather?
Climate refers to long-term records, trends and averages; what one would expect the weather to be like. This is usually determined by examining weather conditions over a long period of time. Weather is the day to day experience of what is actually happening at a particular time.
What is the Beaufort Scale?
The Beaufort Scale was devised by Admiral Sir Francis Beaufort in 1805/06. It is a way of estimating the wind strength according to the appearance of the sea (or on land, largely by the response of trees).
Beaufort Scale for Marine and on Land
How is wind measured?
Direction
The direction of the wind is referred to by the points of the compass, from which the wind blows, for instance, northerly, south-easterly, westerly. An easterly wind is one that comes from the east. Winds are often described in terms of a change in direction. A northerly wind may be said to be veering east, or backing west. A backing wind is one that will move its direction back around the compass (anticlockwise). A wind that veers changes its direction clockwise around the compass points.
The wind’s direction is measured using a wind vane and can be recorded on a wind rose by shading a square, corresponding to the direction from which it blows.
Speed
An anemometer or ventimeter is used for measuring speed in kilometres or miles per hour. The faster the wind blows, the faster the cups on an anemometer spin, or the higher the disc rises inside a ventimeter. The Beaufort Scale is useful to indicate the strength of the wind. Wind instruments should be kept clear from walls, fences and houses, as these will interfere with the speed reading and the wind’s direction becomes difficult to ascertain.
Can you tell me about weather reports?
Readings are taken hourly at all our weather stations. Wind direction and speed, dry bulb and wet bulb temperatures from which humidity is calculated, atmospheric pressure and tendency, cloud amounts and types and heights, visibility, the current or present weather during the hour and also weather that has occurred over the previous three hours, known as the past weather. The readings are coded and entered into a PC where they are quality controlled before being transmitted via modem to Glasnevin in Dublin.
Can you write me a weather report for a car accident?
A legal report for an insurance claim or similar needs to be specially prepared by one of the meteorologists in our Climate Enquiries office. Legal Reports Information and the Legal Weather Report Request form is here. A list of our charges for this service is available here.
What kind of careers are there in Met Éireann?
Met Éireann has two entry grades:
- Meteorologist
- Meteorological Officer
What kind of work does a Meteorologist do?
A Meteorologist is concerned with the assessment and analysis of weather information. Duties include investigation and research into the physical nature of the laws governing air movement, pressure, and temperature changes to determine the causes which bring about the various atmospheric conditions. Analysing and summarising weather data for the purpose of preparing weather maps and forecasting weather changes are also part of a Meteorologist duty.
What kind of work does a Meteorological Officer do?
A Meteorological Officer performs the basic technical duties in the Meteorological Service. These duties include the performance of weather observations, the care and maintenance of meteorological instrumentation and communications facilities, computer operations and computer programming.
Vacancies in Met Éireann will be posted on Publicjobs.ie and on our Vacancies page
Can I do my internship or student placement with Met Éireann?
Unfortunately we are not in a position at present to accept any students on work placement.