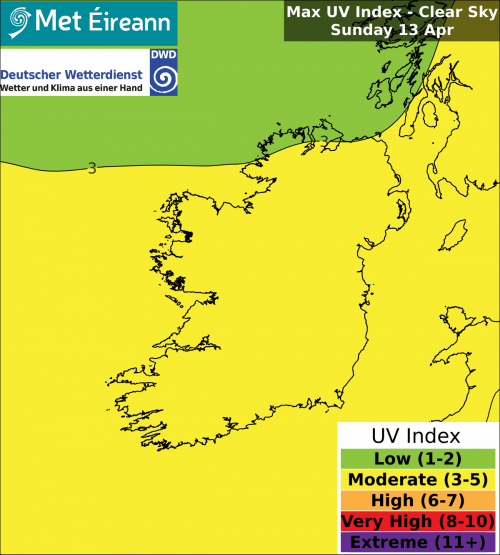
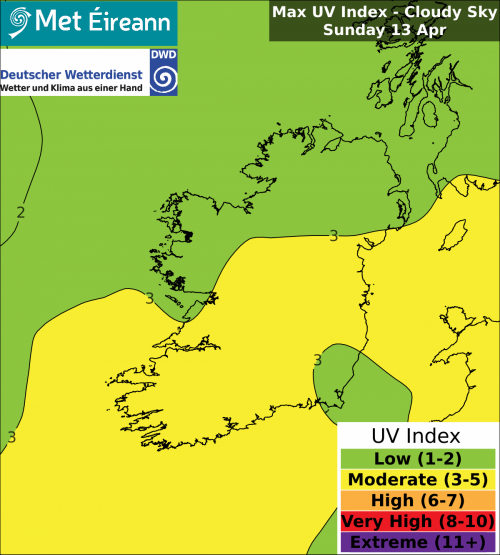
The UV Index maps for Ireland display the maximum UV level forecast under either clear or cloudy sky during the day indicated. The UV Index legend and Advice chart is below. The UV index across Europe can be found at DWD UV Index.
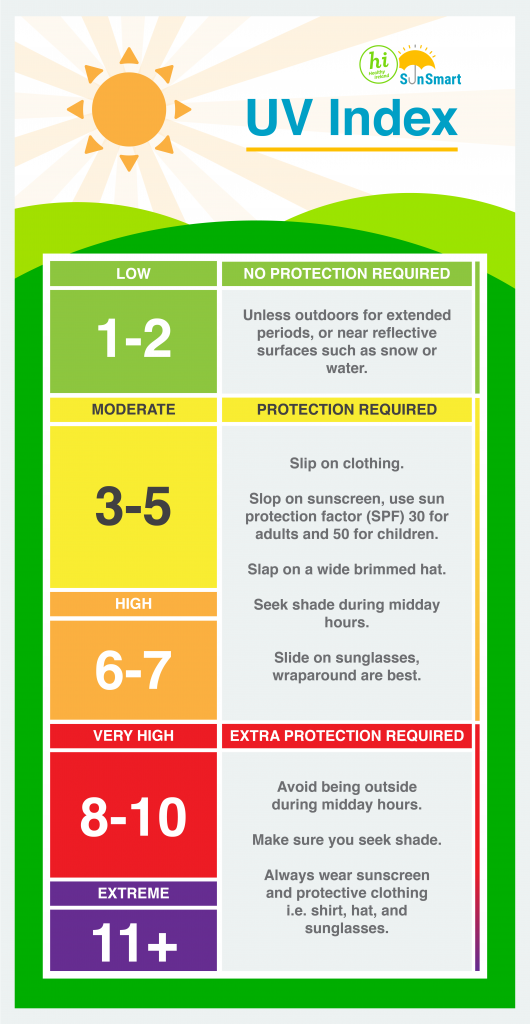
UV Index and Advice
UV Radiation
What is UV?
Ultraviolet radiation (UV) radiation is a type of energy produced by the sun and artificial sources, such as sunbeds and arc welders.
UV radiation is made up of UVA, UVB and UVC rays. All UVA and most of UVB rays reach the earth’s surface. All UVC rays are absorbed by the ozone layer and do not reach the earth’s surface.
You can see sunlight and feel the sun’s heat. But you cannot see or feel the sun’s UV rays. UV can reach you directly from the sun. It can also be reflected off different surfaces and scattered by particles of air.
What are the risks from UV?
Ultraviolet rays (UVA and UVB) from the sun and sunbeds are the main cause of skin cancer. Too much UV exposure also causes sunburn, tanning, premature ageing and eye damage.
When skin and eyes are exposed to UV, this causes DNA damage that is often not properly repaired by your body. Continued UV exposure and damage to your skin builds up over time and can lead to skin cancer.
Who is most at risk of skin cancer?
Those with fair skin are at increased risk of skin cancer. Over 75% of our population have ‘Celtic skin type’ where we freckle and burn easily. We tan with difficulty, or not at all and we carry the highest risk of getting skin cancer. People of all skin types can develop skin cancer.
Outdoor workers are exposed to increased levels of UV rays when working outdoors, this increases their risk of getting skin cancer. Outdoor workers can be exposed to between 2-3 times more UV than indoor workers can.
For more information on how employers and employees can work together, to protect themselves from UV in their workplace go to https://www.hse.ie/sunsmart
What is the UV index?
The UV index is a good indicator of when the sun is most dangerous. It measures the strength of the sun’s UV rays so that you know how and when to protect your skin when outdoors. The higher the UV index, the higher the risk of skin and eye damage.
UV is always strongest during the middle of the day, typically between the hours of 11:00am-3:00pm during April to September.
When the UV index is 3 or above, you need to protect your skin and eyes and follow the Healthy Ireland SunSmart 5 S’s . You can check the UV index forecast in your area here.
The UV index varies depending on where you are in the world, the time of year, the time of day, cloud cover, altitude and surrounding surfaces. The UV is not always strongest when it is hottest.
How to Be SunSmart:
Protect your skin and eyes from ultraviolet radiation from the sun
Follow the Healthy Ireland SunSmart 5’Ss from April to September:
For more information on skin cancer prevention visit https://www.hse.ie/sunsmart
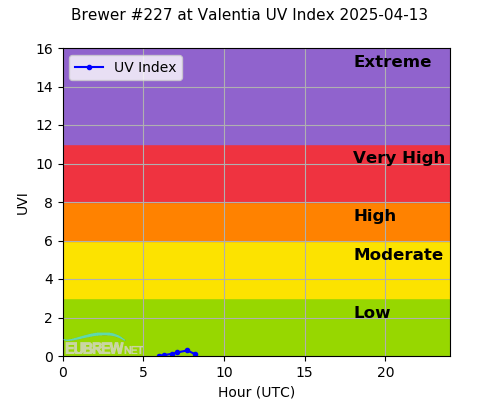
Ultraviolet radiation (UV) is a component of sunlight. The Global Solar UV index is a scale that was developed by the World Health Organisation which measures the UV radiation level at the surface of the Earth, and gives an indication of the potential for skin damage. The graph above shows the current UV Index level as measured at Valentia Observatory Co. Kerry (time is UTC). Further information below.
Data from the Valentia UV Index may be intermittent.
The latest visible Satellite image is the black and white version of the satellite image available here
The UV Index level for your location is included in each of our Regional Weather Forecasts during summer months.
Further Information
- The UV index forecast for Ireland is sourced by Deutscher Wetterdienst and is included in our regional forecasts all year round, but be aware it can only be an average for any one day over the entire country. The clear/sunny sky peak UVI index is reduced by cloud cover.
- For example when the sky is cloud free (sunny) everywhere in Ireland then the UVI for Ireland is high (7.5) in June/July between 11am and 4pm. If it is cloudy everywhere then the UVI is low to moderate (3 to 4).
- Often however the cloud is variable from place to place and from time to time in Ireland and due to wind chill it can often feel cool in summer. Nonetheless a 20 minutes sunny interval can produce sunburn.
- Further details on Ozone Monitoring and the Brewer spectrophotometer is here