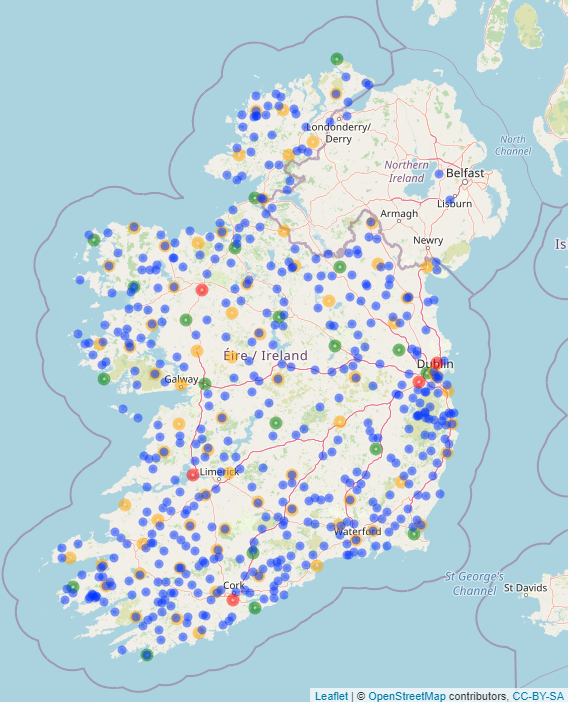
Met Éireann’s Weather Observation Network
Met Éireann has an observation network that gathers weather data across the country for use in weather forecasts, aviation, marine, agriculture, climate analysis, forecast verification and meteorological research. All weather observations record day-to-day changes of the atmosphere and are quality controlled and archived in Met Éireann’s database to formulate long-term climate records.
These data comes in a variety of forms and are obtained from a number of different sources: human reports, in situ instruments and remote sensors. Met Éireann currently uses four different types of weather station to record data, all differentiated according to the range of instruments and measurement interval. Each of these is explained in more detail below:
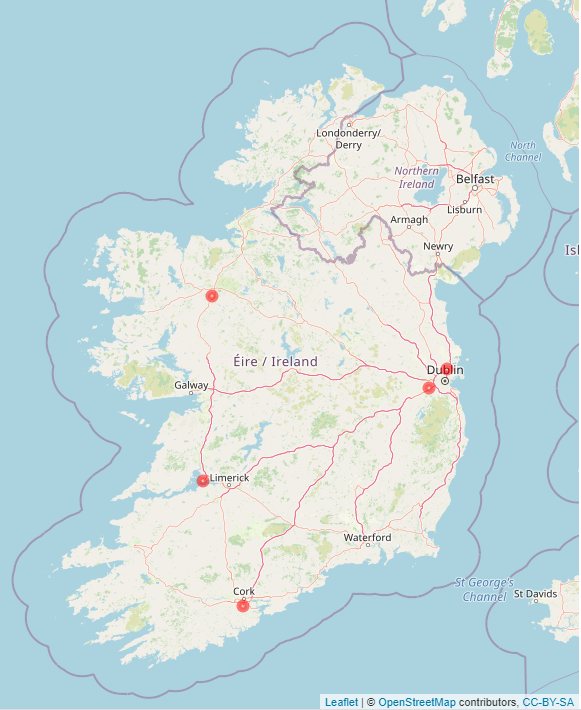
Manned Weather Stations
There are five manned weather stations in operation, Casement Aerodrome, Cork Airport, Dublin Airport, Knock Airport and Shannon Airport . These stations record meteorological elements on an hourly basis. Data are gathered by a meteorological observer and immediately translated into synoptic coding (which is the numerical code for reporting weather observations) and sent via computer to Met Éireann Headquarters (HQ) in Glasnevin, Dublin. See Figure 1.
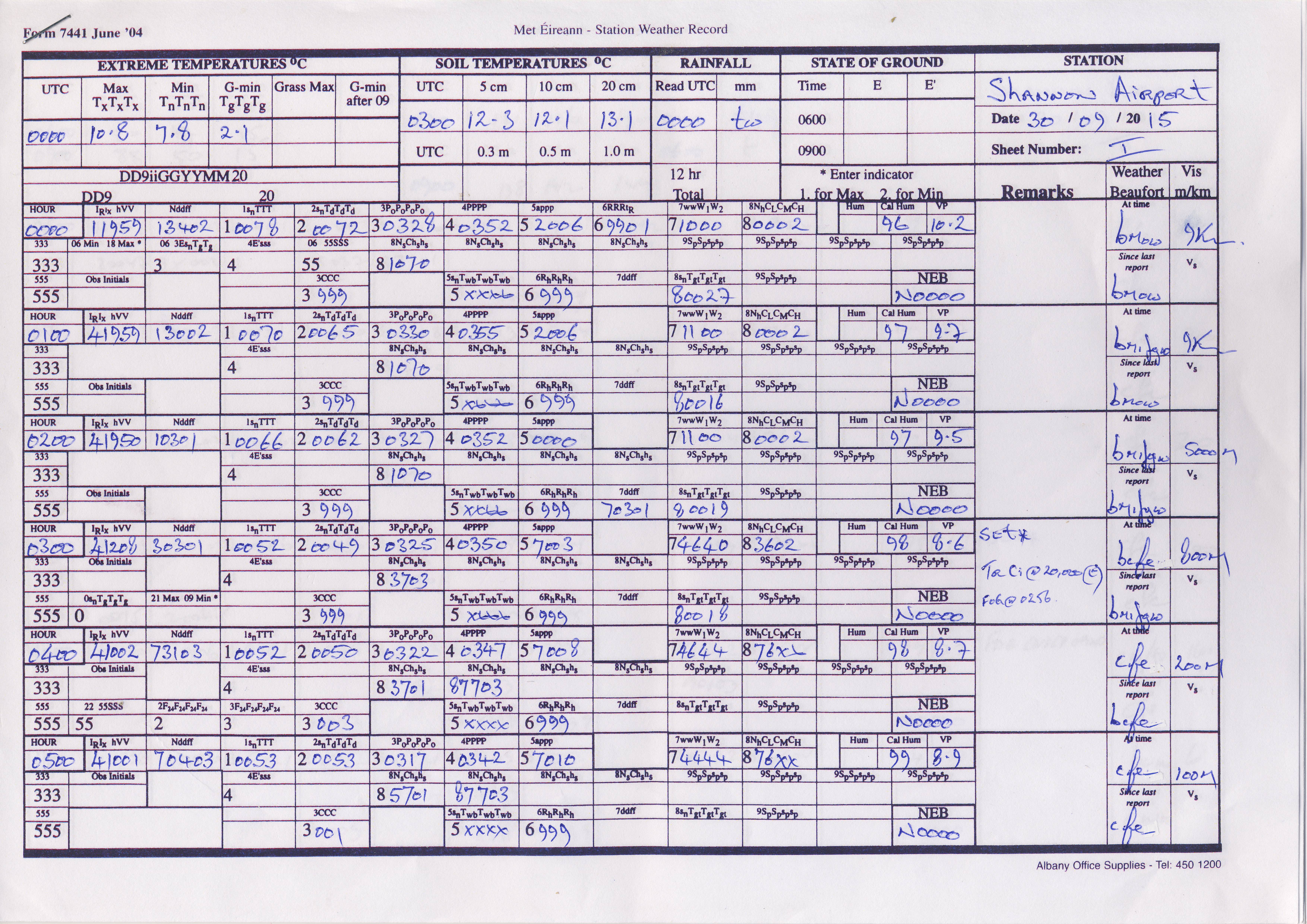
Figure 1: 7441 form used by a meteorological observer to record synoptic coding for each observation.
These data are immediately used in the production of up-to-date weather forecasts. The elements recorded are:
-
- Air temperature
- Rainfall
- Wind speed and direction
- Atmospheric pressure
- Relative humidity
- Soil and earth temperatures
- Past and present weather
- Cloud type and height-Visibility
- Sunshine
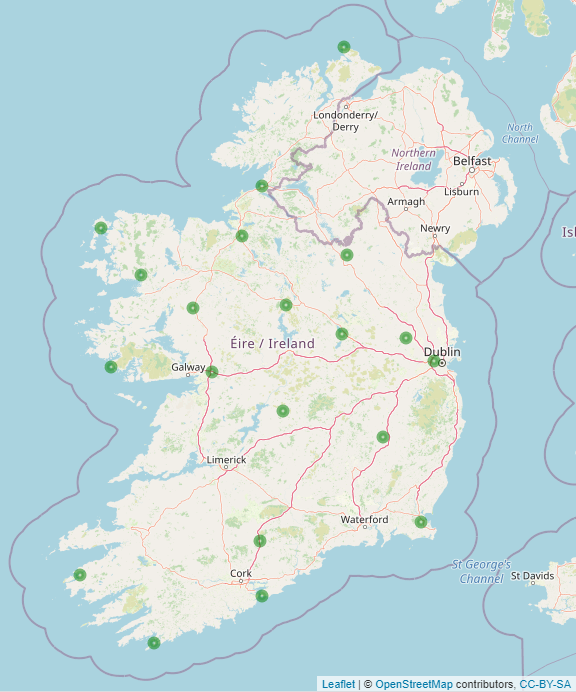
Automatic Weather Stations
There are 20 fully automatic weather stations across the country recording meteorological elements on a minute-by-minute basis. These data are transferred back at hourly intervals via PSTN/broadband line to Met Éireann HQ. They are then analysed by computer programs and an hourly observation is created and translated into synoptic code. These, like the manual observations, are put to immediate use in forecast model runs. The weather elements recorded are the same as those recorded at manned synoptic stations. Automatic weather stations.
The observations from these weather stations can be viewed on Current Observations, Yesterday’s Weather, Daily Data and our Weather Observations Website WOW-IE

Figure 2: Automatic Weather Station at Malin Head, Co. Donegal.
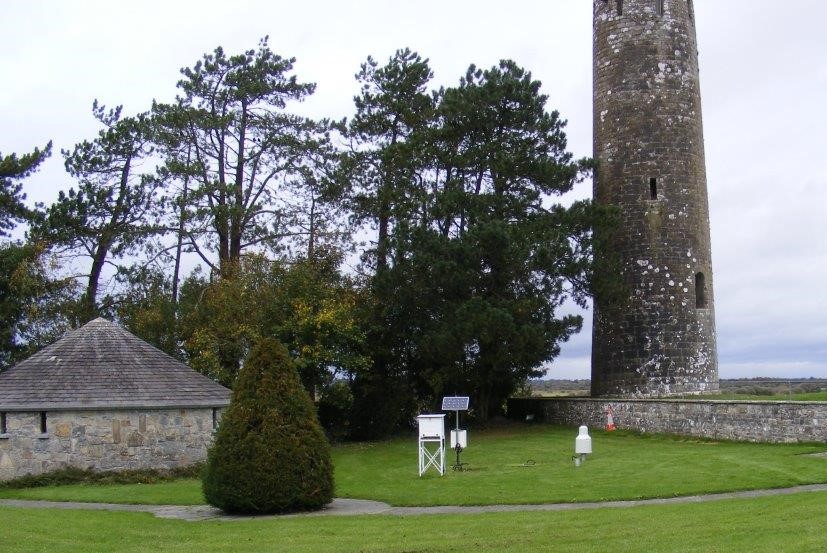
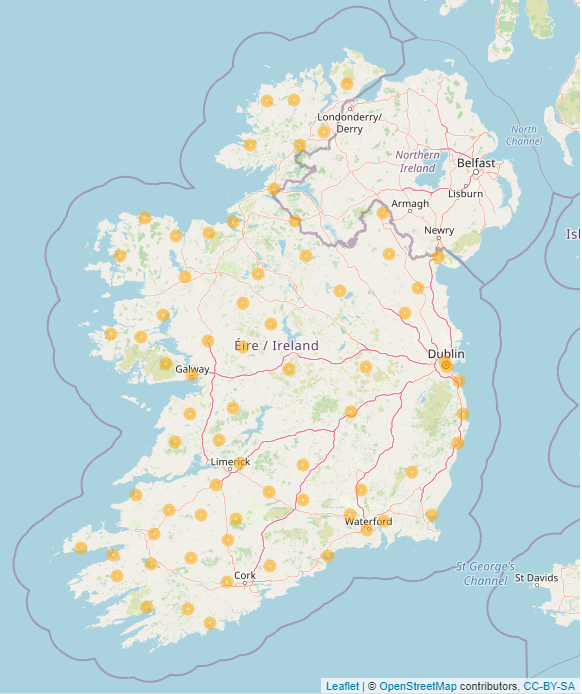
Climatological Stations
Met Éireann’s network of climatological stations has undergone significant change since 2017 with the automation of the climate station network. Mercury thermometers are no longer used, in compliance with the Minamata convention on banning mercury products. Electronic temperature and humidity sensors are now used along with an automatic rainfall gauge. The information from these sensors are recorded, stored and transmitted to Met Éireann HQ for input into the Met Éireann database. Minute by minute data is available as well as daily maxima and minima for temperature, and daily rainfall totals and intensities. These data are used for climate analysis and meteorological research after being quality controlled.
All stations report air temperature, grass temperature, humidity and rainfall. Some stations also report soil and earth temperatures at depths varying from 5cm to 1m.
The observations from these weather stations can be viewed on our Weather Observations Website WOW-IE
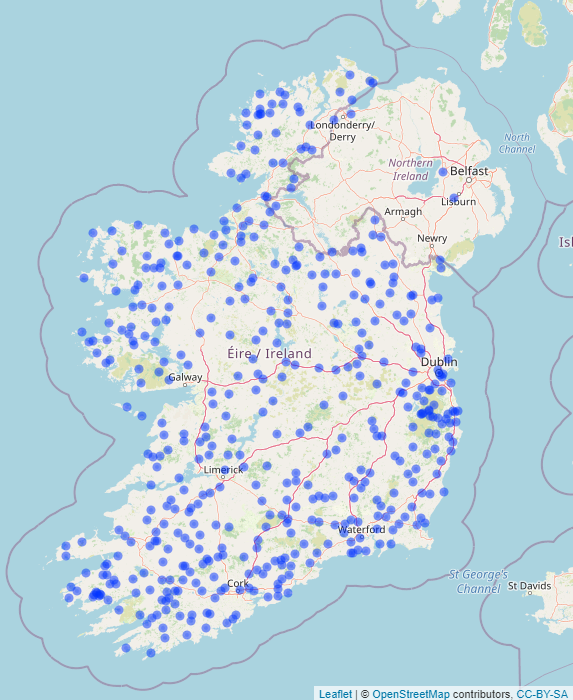
Rainfall Stations
Distribution of rainfall over Ireland is extremely variable so it is important to have countrywide coverage of rainfall instrumentation. Currently there are around 500 rainfall stations across the country, strategically located. These stations, like climate stations, are run by a combination of voluntary observers and state agencies. There are two types of rainfall station; daily and monthly. Daily rainfall stations record rainfall data once a day at 0900 UTC. Rainfall readings at monthly stations are taken once a month at 0900 UTC on the first day of the following month. Both daily and monthly station data are logged on a rainfall card, which is then sent into Met Éireann HQ via post at the end of each month. These data go through the same process as the weather data received from climate stations by being inputted into Met Éireann’s database and quality controlled before being used elsewhere.
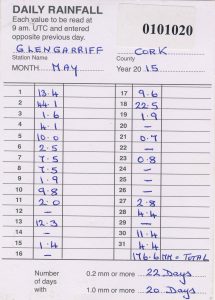
Rainfall card for a daily rainfall station which is sent into Met Éireann at the beginning of the next month.
In the future, all stations will eventually become automatic, resulting in more data readings improving meteorological research and climate analysis.